Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Microelectronics, Xidian University, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710071, P. R. China
In this paper, two optimized autofocusing metasurfaces (AFMs) with different desired focal distances are designed by using particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. Based on the finite element simulation software COMSOL Multiphysics, the performance of ultrasound transducer (UT) with AFM at different design parameters in Airy distributions and the bottom thickness (d) of AFM are simulated and analyzed. Based on the simulation data, the artificial neural network model is trained to describe the complex relationship between the design parameters of AFM and the performance parameters of UT. Then, the multiobjective optimization function for AFM is determined according to the desired performance parameters of UT, including focal position, lateral resolution, longitudinal resolution and absolute sound pressure. In order to obtain AFMs with the desired performance, PSO algorithm is adopted to optimize the design parameters of AFM according to the multiobjective optimization function, and two AFMs are optimized and fabricated. The experimental results well agree with the simulation and optimization results, and the optimized AFMs can achieve the desired performance. The fabricated AFM can be easily integrated with UT, which has great potential applications in wave field modulation underwater, acoustic tweezers, biomedical imaging, industrial nondestructive testing and neural regulation.
Autofocusing metasurface ultrasound transducer optimization Journal of Advanced Dielectrics
2024, 14(1): 2350001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
2 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, School of Physics, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
3 School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China
4 e-mail: liuwm@shanghaitech.edu.cn
We report the ultrafast photocarrier dynamics and coherent phonon excitation in type-II Dirac semimetal platinum ditelluride () thin films via femtosecond (fs) pump-probe spectroscopy at room temperature. Quantitative analysis revealed that the incoherent electronic relaxation consists of two components: a subpicosecond fast relaxation process and a slow component with a time constant of hundreds of picoseconds (ps). Furthermore, the launch of a coherent acoustic phonon (CAP) in the 20 nm film but absence in the 6.8 nm film uncovers the dominant role of temperature gradient in producing a strain wave. The sound velocity and Young’s modulus in the thick are determined to be 1.736 km/s and 29.5 GPa, respectively. In addition, the coherent optical phonon (COP) with a frequency of 4.7 THz corresponding to Te atoms out-of-plane vibration has been well resolved in all films, which is ascribed to displacive excitation of coherent phonon (DECP). The observation of a strong probe-wavelength dependent COP amplitude reveals the resonant feature of the optical excitation-induced atomic displacement in . Our findings provide deep insight into the excitation and dynamics of CAP and COP as well as the photocarriers’ recovery pathway and lifetimes in . Our study also demonstrates that the COP spectroscopy is a powerful tool to reveal the modulation of frequency-dependent optical constants induced by atomic vibrations, which may find applications in the fields of optoelectronics and ultrafast photonics.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(3): 03000653

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
2 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, School of Physics, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
3 School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China
4 e-mail: liuwm@shanghaitech.edu.cn
We report the ultrafast photocarrier dynamics and coherent phonon excitation in type-II Dirac semimetal platinum ditelluride () thin films via femtosecond (fs) pump-probe spectroscopy at room temperature. Quantitative analysis revealed that the incoherent electronic relaxation consists of two components: a subpicosecond fast relaxation process and a slow component with a time constant of hundreds of picoseconds (ps). Furthermore, the launch of a coherent acoustic phonon (CAP) in the 20 nm film but absence in the 6.8 nm film uncovers the dominant role of temperature gradient in producing a strain wave. The sound velocity and Young’s modulus in the thick are determined to be 1.736 km/s and 29.5 GPa, respectively. In addition, the coherent optical phonon (COP) with a frequency of 4.7 THz corresponding to Te atoms out-of-plane vibration has been well resolved in all films, which is ascribed to displacive excitation of coherent phonon (DECP). The observation of a strong probe-wavelength dependent COP amplitude reveals the resonant feature of the optical excitation-induced atomic displacement in . Our findings provide deep insight into the excitation and dynamics of CAP and COP as well as the photocarriers’ recovery pathway and lifetimes in . Our study also demonstrates that the COP spectroscopy is a powerful tool to reveal the modulation of frequency-dependent optical constants induced by atomic vibrations, which may find applications in the fields of optoelectronics and ultrafast photonics.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(3): 03000661
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所 发光学及应用国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 吉林大学材料学与工程学院 汽车材料教育部重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130012
4 澳门大学应用物理与材料研究所 教育部联合重点实验室, 中国 澳门 999078
碳点由于其低毒性、易制备、良好的光稳定性及可调的发光等特性有望成为一类理想的新型固态发光材料。然而,由于聚集诱导荧光猝灭(ACQ)效应的存在,使得碳点在固态发光领域的发展受到了限制,因此制备具有抗ACQ效应的固态发光碳点是碳点研究领域的一个重要方向。本文根据固态发光碳点研究的最新进展,从碳核、表面态调控、超分子及聚合物交联增强发光方面分类总结了具有抗ACQ效应固态发光碳点的制备方法及光物理性质,探讨了其实现固态发光的物理机制。此外,还介绍了该类碳点在固态发光领域的应用进展,并对固态发光碳点的发展现状和所面临的问题进行了讨论。
碳点 聚集诱导荧光猝灭 固态发光 发光二极管 carbon dots aggregation-induced fluorescence quenching solid-state luminescence light emitting diode
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所发光学与应用国家重点实验室,吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 澳门大学应用物理与材料研究所教育部联合重点实验室,澳门 999078
碳纳米点由于具有独特的发光特性、良好的生物相容性、低毒性、良好的光稳定性等特性在近年来被广泛关注。这些特性使其在光电器件、可见光通讯、肿瘤治疗、生物成像等领域拥有潜在的应用价值。受到原料和合成方法的影响,碳纳米点材料体系多种多样。本文将系统地综述本课题组近年来以柠檬酸和尿素为主要原料合成的氮掺杂碳纳米点及其物理化学性质,探讨碳纳米点能带调控的方法及原理,并介绍碳纳米点的应用研究进展。
碳纳米点 氮掺杂 发光材料 carbon nanodots nitrogen doping photoluminescent materials 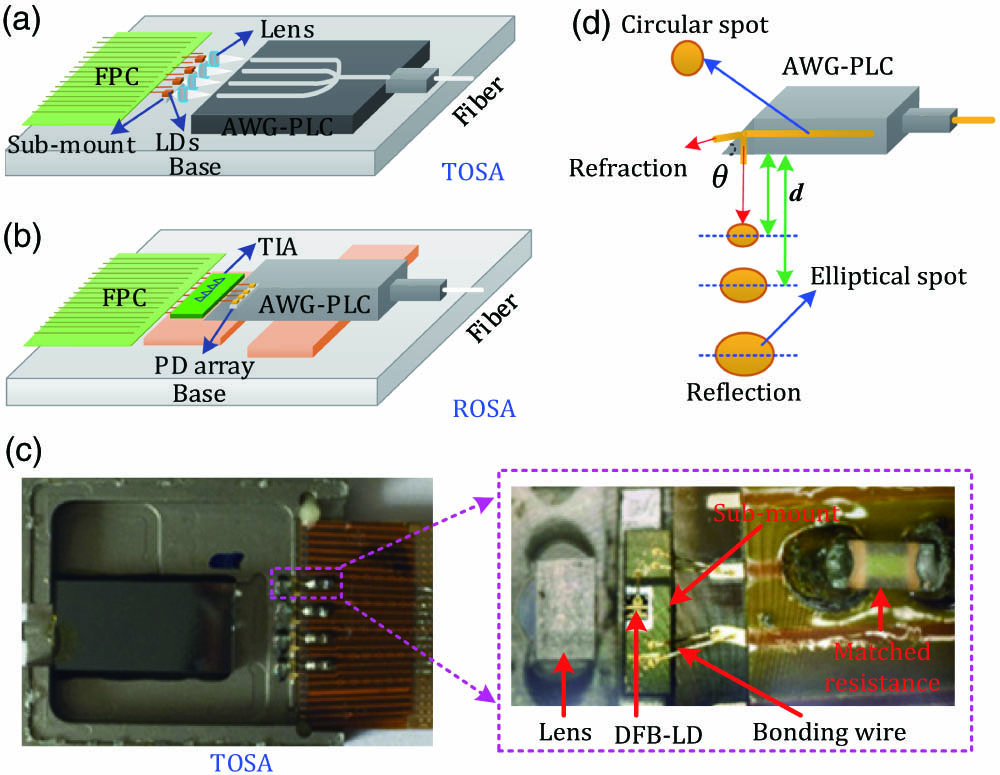
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic Information and Communications, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics and School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
In this paper, an integrated compact four-channel directly modulated analog optical transceiver is proposed and fabricated. The 3 dB bandwidth of this optical transceiver exceeds 20 GHz, and the measured spurious-free dynamic range is up to . The optical coupling efficiency (CE) is improved by using a precise submicron alignment technique for lens coupling in a transmitter optical subassembly, and the highest CE is achieved when the oblique angle of the arrayed waveguide grating using a silica-based planar lightwave circuit (AWG-PLC) in receiver optical sub assembly is set to 42°. Based on the proposed optical transceiver, we have experimentally demonstrated a 6.624 Gbit/s multi-input multioutput (MIMO) 16-quadrature amplitude modulation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (16QAM-OFDM) radio signal over 15.5 km standard single mode fiber, together with 1.2 m wireless transmission in both an uplink and a downlink. To cope with the channel interference and noise of the fiber-wireless transmission system, a low-complexity MIMO demodulation algorithm based on lattice reduction zero-forcing (LR-ZF) is designed. In our experiment, 1.6 dB power penalty is achieved by using the proposed LR-ZF algorithm, compared to the commonly used zero-forcing algorithm. Moreover, this LR-ZF algorithm has much less complexity than the optimal maximum-likelihood sequence estimation (MLSE) at a given transmission performance. These results not only demonstrate the feasibility of the integrated optical transceiver for MIMO fiber-wireless application but also validate that the proposed LR-ZF algorithm is effective to eliminate the interference for hybrid fiber-wireless transmission.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(12): 12001461
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所 发光学及应用国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 澳门大学 应用物理与材料工程研究所, 中国 澳门 999078
碳点作为一种新型的碳基荧光纳米粒子由于其可调谐发光、高光稳定性、生物相容性和低成本等独特优势而引起了很多关注。在过去的十几年中, 碳点的制备和应用取得了巨大进展。然而, 由于前体和合成方法的多样性, 碳点的光致发光机理具有很大争议。现在人们普遍认为, 碳点的光致发光源于电子在带隙的跃迁, 并将荧光起源分别归结为碳核跃迁(π-π*)、表面态跃迁(n-π*)以及分子荧光团等。本文总结了碳点发光起源的几种可能和机制, 分别讨论了通过调控碳点粒径以及进行表面工程处理的方法来实现碳纳米点带隙可调控的高效发光。介绍了通过表面工程、元素掺杂等手段提升碳纳米点光致发光量子产率及其在光电器件、信息存储、生物成像、光热治疗以及光动力治疗中的应用。
碳纳米点 光致发光机理 带隙调控 生物成像 白色发光二极管 carbon dot photoluminescence mechanisms bandgap modulation bioimaging white-light-emitting devices
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所 发光学及应用国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
碳纳米点(碳点)是一种新型的纳米发光材料, 具有优异的发光性能、良好的生物相容性、低毒性、水溶性好和表面易功能化等特性, 在光电器件、生物成像、光热治疗等领域展现了潜在应用价值。然而, 合成碳点的前驱体材料多种多样, 合成方法各有不同, 导致其发光机理复杂多样。本文主要针对使用柠檬酸作为碳源、尿素或氨水作为氮源, 采用微波和溶剂热的合成方法制备的氮掺杂碳点, 探索碳点的发光机理和抑制碳点聚集诱导荧光猝灭的方法, 并进一步研究碳点在固态照明、可见光光通讯、生物成像和光热治疗等领域的应用前景。
氮掺杂碳纳米点 发光机理 固态照明 生物成像 光热治疗 nitrogen doped carbon nanodots luminescence mechanism solid lighting biological imaging heat treatment
1 吉林大学 口腔医院, 吉林 长春130021
2 吉林大学 第二医院, 吉林 长春130000
3 中国科学院 长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 吉林 长春 130033
碳纳米点作为新兴的碳纳米材料, 具备制备成本低、尺寸小、低毒、生物相容性高、水溶性好、易修饰、光物理性质独特等诸多优点, 在生物医疗领域展现了独有的优势和应用前景。由于具有丰富的表面官能团, 碳纳米点可以与靶向配体、医学影像造影剂、核酸、化学药物、光敏剂、光热转换试剂等功能性诊断治疗试剂相互作用形成复合物。目前, 碳纳米点及其复合物在医学影像、基因治疗、化学药物治疗、光热、光动力治疗等生物医学诊断治疗领域的应用正在被广泛的开发和报道。这些工作对开发基于碳纳米点的医学诊断治疗试剂及其临床推进具有重要意义, 为推进人类重大疾病的个体化、可视化、非入侵式、小损伤的诊断治疗提供一种新的药物体系。本文将关注应用于诊断治疗领域的碳纳米点及其复合物的设计、构建及性能研究, 对已报道的基于碳纳米点的诊断治疗试剂在生物医疗领域的研究进展进行总结和讨论。
碳纳米点 碳纳米点复合物 诊断治疗试剂 纳米医疗 carbon nanodots carbon nanodot complexes theranostic agents nanomedicine
1 西安建筑科技大学冶金工程学院, 陕西 西安 710055
2 西安建筑科技大学环境与市政工程学院, 陕西 西安 710055
半导体光催化氧化技术在处理能源危机和环境污染问题方面有非常重要的应用。 选取石墨烯对水热法制备的Zn2SnO4进行改性。 通过透射电镜(TEM)观察其形貌特征, 通过X射线衍射(XRD)、 红外光谱(FTIR)、 拉曼光谱(Raman)以及X射线光电子能谱(XPS)分析其结构和组成。 采用紫外-可见光分光光度计检测石墨烯/Zn2SnO4催化降解亚甲基蓝(MB)性能。 通过添加自由基捕获剂的光催化实验、 电子顺磁共振谱和荧光光谱检测分析石墨烯/Zn2SnO4降解MB的光催化机理。 通过光催化重复性实验对石墨烯/Zn2SnO4的稳定性进行评估。 结果表明: 加入石墨烯不会对Zn2SnO4的结构形貌产生较大影响; 当氧化石墨烯(GO)添加量为4 Wt%时, 石墨烯/Zn2SnO4的光催化活性最高的; 光催化过程中·OH是主要的活性物质, 存在·OH间接氧化有机污染物的机制。
石墨烯 锡酸锌 光谱特性 亚甲基蓝 光催化 羟基自由基 Graphene Zn2SnO4 Spectral characteristic Methylene blue Photocatalysis Hydroxyl radical 光谱学与光谱分析
2018, 38(4): 1219





